Osteoporosis, from the Greek “porous bones,” results from an imbalance in the continual process of bone remodeling. In this condition, aged bone cells are destroyed more rapidly than new ones are formed, leading to weakened and fragile bones susceptible to fractures. Here, we explore the interplay between osteoporosis and the endocannabinoid system, offering insights into potential treatment approaches.
Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is characterized by a decrease in bone density over time, making the bones more susceptible to stress fractures. The central nervous system plays an essential role in regulating bone metabolism, in both health and disease, through a range of neurotransmitters that influence the activity of bone cells. The root cause of this condition lies in the imbalance between the cells that break down aged bone tissue (osteoclasts) and those responsible for forming new bone tissue (osteoblasts). Osteoporosis is often asymptomatic, but its presence can be linked to several preventable risk factors, such as smoking, menopause, use of corticosteroids, and underlying medical conditions.
In conventional medicine, osteoporosis is primarily managed through pharmaceutical interventions, nutritional modifications (including minerals and vitamin D supplementation), and exercise regimens.
The ECS, Cannabis, and Osteoporosis
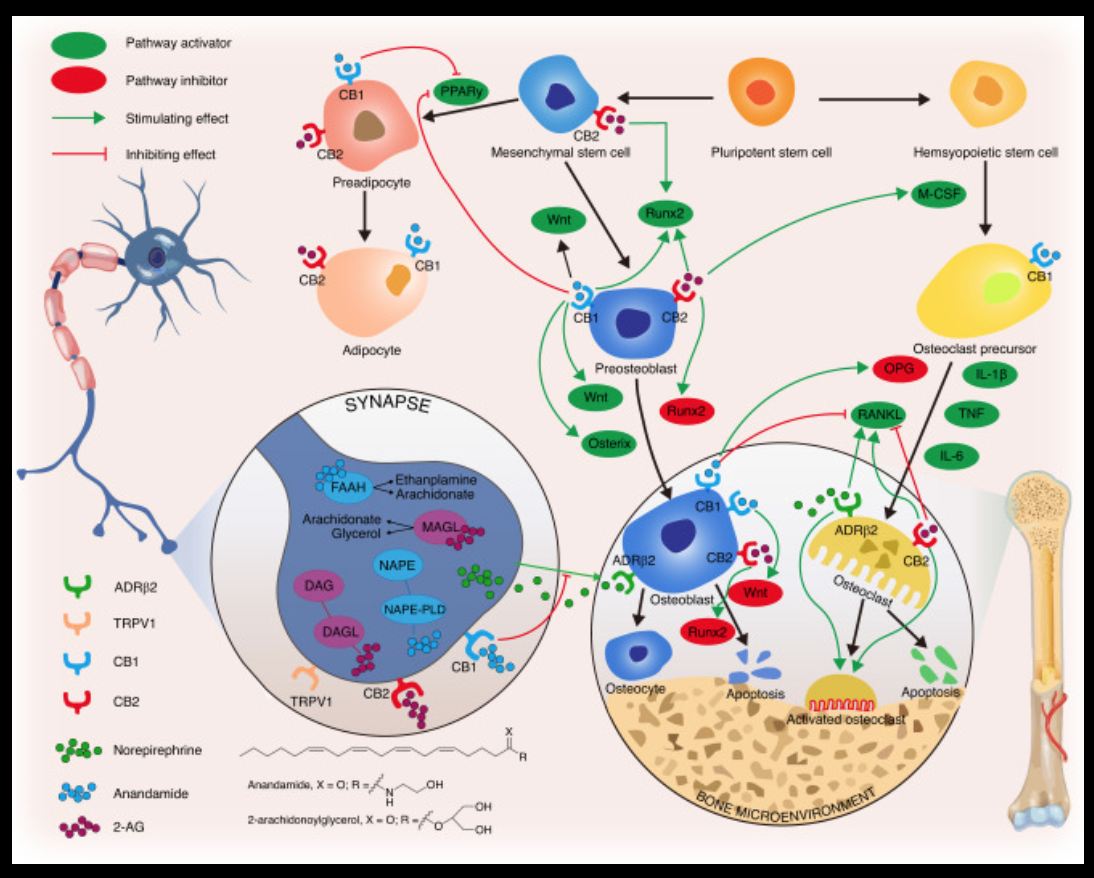
The endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and signaling molecules, plays a significant role in bone health, repair, and maintenance. Several cannabinoid-sensitive receptor sites, including CB1, CB2, GPR55, TRPV1, and TRPV4, have been identified in bone tissue, with CB2 receptor sites being the most abundant.
Endocannabinoids, like anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), can influence osteoblast formation, osteoclast activity, and bone formation. Synthetic cannabinoids have also demonstrated various effects on bone-related activities. For instance, CB2 agonists, such as HU-308 or JWH133, stimulate osteoblast proliferation, while CB2 antagonists, like AM630 or SR144528, inhibit osteoclast differentiation. CBD, an antagonist at GPR-55, increases osteoblast activity but decreases osteoclast function.
Cannabis Research for Osteoporosis
Pre-clinical studies have indicated that the endocannabinoid system, its receptors, enzymes, and primary endocannabinoids are present and functional in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. That suggests a potential avenue for modulating osteoporosis through cannabinoid-based therapies.
Research suggests that both CB1 and CB2 receptor sites may play a role in modulating osteoporosis through different mechanisms. CB2 receptor activation, primarily via specific agonists, appears promising in re-establishing the balance between bone resorption and formation. Activation of CB2 receptors has also shown potential in mitigating ovariectomy-induced bone loss in animal models.
In a 2015 study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, CBD was found to enhance the healing of fractured bones in rats. Similarly, another study in the same journal in 2017 demonstrated that CBD improved bone density and strength in rats with mid-femoral fractures. These findings suggest the therapeutic potential of CBD in bone healing and density improvement.
A review published in the journal Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity in 2017 suggested that the endocannabinoid system, influenced by CBD and related compounds, plays a significant role in bone metabolism. This review further indicated that targeting the endocannabinoid system may hold promise as a treatment strategy for osteoporosis.
A recent 2023 study published in Bone Research delved into the interplay between the nervous system and skeletal interoception. The interplay of sensory nerves in skeletal tissues facilitates the central nervous system’s reception of bone-derived signals and the maintenance of homeostasis. The study also looked at the role of endocannabinoids, including anandamide and 2-AG, which actively influence the bone microenvironment. The CB1 receptor predominantly regulates bone metabolism through sympathetic nerve terminals, suppressing norepinephrine release and enhancing osteoblast activity and differentiation while also reducing osteoclast formation. Additionally, CB1 and CB2 receptors are widely distributed in osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and their precursors, significantly contributing to bone homeostasis.
In conclusion, while research is ongoing, there is accumulating evidence that the endocannabinoid system, especially in conjunction with CBD, may offer novel therapeutic targets for osteoporosis. Further studies are needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks associated with cannabis-based treatments for this condition. If considering cannabis as a potential therapy, it may be prudent to opt for CBD-dominant strains during periods of bone healing.
References
- Clouse G, Penman S, Hadjiargyrou M, Komatsu DE, Thanos PK. Examining the role of cannabinoids on osteoporosis: a review. Arch Osteoporos. 2022 Nov 19;17(1):146. doi: 10.1007/s11657-022-01190-x. PMID: 36401719.
- Idris AI. Role of cannabinoid receptors in bone disorders: alternatives for treatment. Drug News Perspect. 2008 Dec;21(10):533-40. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2008.21.10.1314055. PMID: 19221634.
- Kulpa J, Harrison A, Rudolph L, Eglit GML, Turcotte C, Bonn-Miller MO, Peters EN. Oral Cannabidiol Treatment in Two Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia: A Case Series. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023 Sep;8(S1):S83-S89. doi: 10.1089/can.2023.0060. PMID: 37721991.
- Kogan NM, Mechoulam R. Cannabinoids in health and disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2007;9(4):413-430. PMID: 18286801 PMCID: PMC3202504. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2007.9.4/nkogan.
- Saponaro F, Ferrisi R, Gado F, Polini B, Saba A, Manera C, Chiellini G. The Role of Cannabinoids in Bone Metabolism: A New Perspective for Bone Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):12374. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212374. PMID: 34830256; PMCID: PMC8621131.
- Xiao Y, Han C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Bao R, Li Y, Chen H, Hu B, Liu S. Interoceptive regulation of skeletal tissue homeostasis and repair. Bone Res. 2023 Sep 5;11(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00285-6. PMID: 37669953; PMCID: PMC10480189.
- Xin Y, Tang A, Pan S, Zhang J. Components of the Endocannabinoid System and Effects of Cannabinoids Against Bone Diseases: A Mini-Review. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 19;12:793750. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.793750. PMID: 35126132; PMCID: PMC8815309.

Made in California, with the finest ingredients, bcure products are made one by one with the highest quality control.

